In the heart of the North Caucasus lies Ingushetia, a region often overshadowed by its more renowned neighbors yet steeped in enchanting history and cultural richness. With its landscape marked by the imposing Greater Caucasus mountains and dotted with ancient watchtowers, Ingushetia presents an intriguing blend of natural splendor and human heritage. As the home of the Ingush people, the region offers a tapestry of traditions and a unique culinary palette that intrigues the discerning traveler.
Ingushetia in Russia’s North Caucasus

Nestled in the North Caucasus region of Russia, Ingushetia is often overshadowed by its more renowned neighbors yet possesses a unique charm. This small republic boasts a rich cultural heritage and stunning natural beauty, making it an intriguing destination for those seeking an uncharted path.
Tourism in Ingushetia is gradually gaining attention for its authentic experiences that reflect the essence of Caucasus traditions. Visitors are captivated by the enchanting Ingush folklore, which offers insights into the lives of its people.
Cultural Traditions
Storytelling, music, and dance are central to these traditions, passed down through generations. The allure of Ingushetia is further enhanced by its regional cuisine, where flavors narrate the land’s bountiful offerings—dishes like lamb stews and flatbreads highlight local ingredients.
Historical Landmarks
Ingushetia is home to remarkable historical sites, including ancient watchtowers and medieval Christian churches that stand as silent witnesses to the region’s tumultuous past. For adventurous travelers, Ingushetia promises a journey of discovery, revealing hidden treasures.
Set against the dramatic backdrop of the Greater Caucasus mountain range, Ingushetia’s geography significantly influences its cultural and demographic identity. The region is primarily inhabited by the Ingush people, a largely Muslim ethnic group that embodies a unique blend of tradition and modernity.
The interplay between rugged terrain and vibrant communities highlights the distinct character of this often-overlooked Russian republic. The Greater Caucasus itself stretches approximately 1,200 kilometers from the eastern shores of the Black Sea to the Caspian Sea, characterized by unique geological formations that create a spectacular landscape rich in biodiversity.
Climate and Ecology
The climate varies considerably along the range; the western part experiences a maritime climate while the eastern sections are subject to a drier continental climate. These variations profoundly impact mountain ecology and the types of species thriving in different areas.
Historically, the Greater Caucasus has served as a crossroads for cultural exchanges. Mountain passes facilitated trade and interaction among diverse communities, enriching the region’s cultural landscape. This blend of natural beauty and cultural diversity makes the Greater Caucasus both a geographic marvel and a significant corridor of human history.
Ingushetia’s population dynamics reflect its commitment to cultural preservation. The Ingush language, customs, and religious rituals are vital components of their way of life. Despite demographic changes over the years, this community has shown remarkable resilience in maintaining its heritage amidst external influences.
The Ingush identity is closely tied to Islamic faith, which plays a crucial role in their cultural practices. The community’s emphasis on cultural preservation is complemented by an adaptive spirit, allowing them to navigate contemporary challenges while holding steadfast to their roots. As Ingushetia continues to evolve, the dedication of the Ingush people to their identity and faith underscores their enduring strength within the diverse ethnic mosaic of the Caucasus.
Historical Background

Ingushetia’s history is significantly shaped by its integration into the Russian Empire in 1810, marking a pivotal moment that influenced future developments. This era was characterized by military conquests and the formation of the Checheno-Ingushetia region, illustrating a complex socio-political landscape.The Soviet era introduced further transformations, leading to various challenges and adaptations in the post-Soviet period. The Russian Empire’s expansion into the Caucasus brought about cultural assimilation and territorial disputes, as local leaders sought to maintain their identity amidst external pressures. The integration efforts led to resistance and adaptation among the Ingush people, who faced economic hardships exacerbated by broader geopolitical issues.Despite these challenges, the Ingush maintained a strong sense of identity and cultural heritage, demonstrating resilience throughout their historical journey.
Timeline of Integration into the Russian Empire
The integration process began in 1810, marked by military conflicts and diplomatic engagements. The Ingush negotiated terms for regional autonomy while navigating the complexities of cultural assimilation. This period was crucial for shaping Ingush history as the community faced external domination and internal preservation.The process involved profound negotiation and adaptation, laying the groundwork for Ingushetia’s ongoing quest to balance integration with cultural preservation.
Formation of Checheno-Ingushetia
Established in 1934, Checheno-Ingushetia emerged from the unification of the Chechen and Ingush Autonomous Oblasts. This dual-ethnic entity highlighted the region’s intricate ethnic identity amid centralized governance pressures. The Chechen Conflict further complicated local governance, challenging efforts to maintain autonomy and cultural preservation.The creation of Checheno-Ingushetia reflects the enduring spirit of its people striving to protect their unique identities amidst external influences.
Soviet and Post-Soviet Times
Soviet policies profoundly affected Checheno-Ingushetia during the mid-20th century. The forced deportations of 1944 disrupted communities, leaving lasting scars. With the Ingush return in the late 1950s, significant economic changes occurred due to imposed industrialization.Following the Soviet Union’s dissolution, Checheno-Ingushetia faced substantial challenges in achieving economic stability and navigating volatile political dynamics. This era also saw a cultural revival as the Ingush sought to reclaim their heritage after years of suppression.Today, Ingushetia continues to address its Soviet legacy while striving for economic growth and political stability.
Cultural Heritage
Ingushetia’s cultural heritage showcases traditional practices and unique customs, prominently featuring its distinctive tower culture. Festivals, music, and dance play vital roles in community life, offering insights into Ingush society.
Traditional crafts such as pottery reflect functional artistry deeply rooted in community identity. Folk medicine emphasizes herbal remedies, showcasing a long-standing relationship with nature. Ritual practices foster communal ties and continuity through unique musical instruments like the pondar.
Storytelling traditions preserve historical narratives and moral teachings, connecting generations through shared wisdom.
Ingush Customs
A defining aspect of Ingush customs is its tower culture, representing architectural legacy. These stone towers symbolize family pride and social status while narrating centuries of history. Traditional dress reflects cultural identity during celebrations, accompanied by folk music that enhances communal gatherings.
Vibrant festivals throughout the year highlight Ingushetia’s rich heritage through music and dance. These events foster unity among communities while showcasing age-old practices alongside contemporary expressions.Traditional attire worn during these festivals is rich in symbolism, reflecting unique identities. The cultural significance extends beyond entertainment; these celebrations are crucial for preserving heritage.
Story telling traditions serve as a living archive for Ingushetia’s history, capturing essential aspects of identity through storytelling. This form of cultural transmission ensures ancestral values resonate within the community while empowering individuals to define their narrative.
Culinary Heritage
Ingushetia’s culinary traditions reflect its cultural identity through local ingredients like lamb and mountain herbs. Traditional recipes emphasize slow-cooking techniques that enhance flavors. Dishes such as zhizhig-galnash are central to communal gatherings, embodying hospitality values.Dining customs express unity and respect through shared meals, bridging past and present while allowing for innovation in modern times. Through its cuisine, Ingushetia celebrates its vibrant heritage.
Economic Activities

Nestled in the North Caucasus, Ingushetia has a rich tapestry of traditional occupations that have sustained its communities for generations. The region is known for its enduring traditional crafts, where skilled artisans produce intricate woodwork, ceramics, and metalwork. These crafts not only preserve cultural heritage but also offer economic opportunities for locals.
Ingushetia’s agricultural practices are deeply rooted in the fertile landscapes that support diverse crops, including grains, vegetables, and fruits, essential to the local diet and economy.
Textile production also holds a significant place in Ingushetia’s traditional occupations, with local weavers creating vibrant fabrics that reflect the region’s distinctive aesthetic. This craft intertwines art with utility, as textiles are used for clothing and domestic purposes.
Music, an integral part of Ingushetian culture, is expressed through folk music, which has been passed down through generations, capturing the spirit and history of the people.
Animal husbandry remains a cornerstone of rural life, with livestock such as sheep and cattle providing meat, dairy, and wool. These practices exemplify the resourcefulness of Ingushetia’s people, who continue to balance tradition with the demands of modern life, fostering a resilient community.
While traditional occupations continue to sustain the people of Ingushetia, the region is increasingly opening its doors to tourism as a means of economic growth. This shift towards emerging tourism is marked by a strategic focus on sustainable tourism, ensuring that the natural and cultural resources are preserved for future generations.
Adventure activities, such as hiking and mountain climbing, attract travelers seeking to explore the rugged landscapes of the Caucasus, providing a sense of freedom and connection with nature.
Natural Beauty
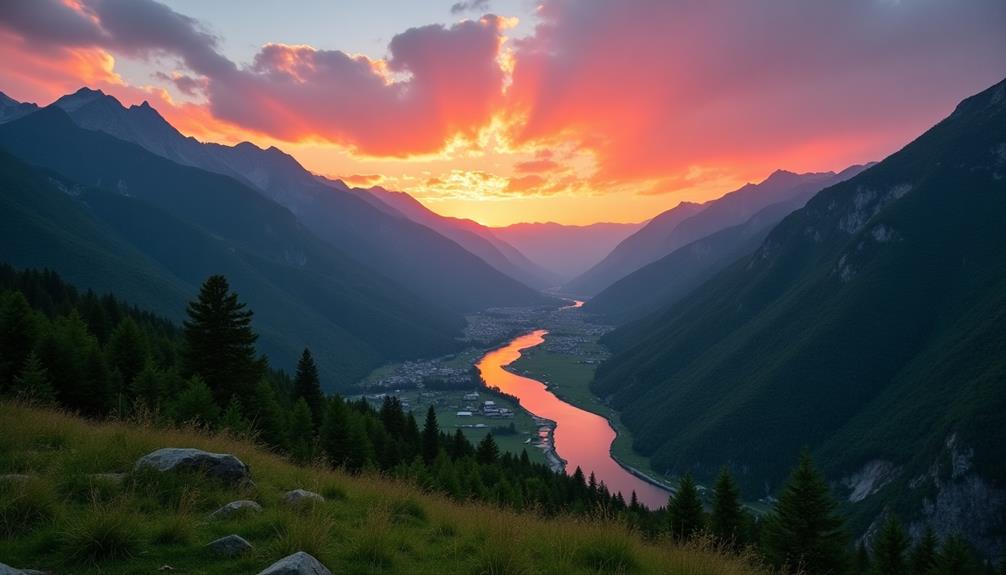
Amidst the rugged terrain of the North Caucasus, Ingushetia boasts a striking tapestry of scenic landscapes that captivate the senses and inspire wonder. The region’s mountain ecosystems are a haven for nature enthusiasts, offering a unique blend of biodiversity and breathtaking vistas. Home to several endemic species, these ecosystems highlight the intricate balance of nature and the importance of conservation efforts to preserve this natural heritage.
Ingushetia’s commitment to maintaining its pristine environment is evident in its well-marked hiking trails, which enable explorers to traverse the majestic peaks and verdant valleys. These trails offer both challenge and serenity, inviting hikers to discover the unspoiled beauty of the Caucasus.
For those with a passion for landscape photography, the region’s dramatic scenery presents countless opportunities to capture nature’s artistry, from mist-cloaked mountains to sunlit meadows.
Efforts to conserve Ingushetia’s landscapes not only protect its rich biodiversity but also guarantee that future generations can experience the region’s untainted allure. As a destination that embodies freedom and natural splendor, Ingushetia stands as a reflection of the enduring beauty of the Caucasus, beckoning travelers to explore its untamed wilderness.

In the vast expanse of Russia’s diverse regions, one finds a unique cultural treasure trove in the Republic of Ingushetia. This small yet vibrant republic serves as an essential repository of Russia’s rich cultural heritage. Ingushetia’s commitment to cultural preservation is evident in its thriving heritage tourism, which attracts visitors enthusiastic to explore its ancient customs and traditions.
Traditional crafts in Ingushetia further underscore the region’s dedication to maintaining its cultural legacy. Artisans continue to create intricate textiles, ceramics, and woodwork, each piece embodying centuries of cultural exchange and innovation.
These crafts not only preserve traditional techniques but also provide a sense of continuity and identity for future generations.
Ingushetia’s unique position within Russia is marked by its ability to balance preservation with modernity. It stands as a beacon of cultural richness amidst a rapidly changing world, offering a compelling narrative of identity and endurance.
For those who seek freedom through cultural exploration, Ingushetia is an unparalleled gateway into the soul of the Caucasus.




